Civil Services in India
Topics
All
Civil Services in India (26)
Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude
» Chapters from Book (11)
» Case Studies (8)
Solved Ethics Papers
» CSE - 2013 (18)
» CSE - 2014 (19)
» CSE - 2015 (17)
» CSE - 2016 (18)
» CSE - 2017 (19)
» CSE - 2018 (19)
» CSE - 2019 (19)
» CSE - 2020 (19)
» CSE - 2021 (19)
» CSE -2022 (17)
» CSE-2023 (17)
Essay and Answer Writing
» Quotes (34)
» Moral Stories (18)
» Anecdotes (11)
» Beautiful Poems (10)
» Chapters from Book (5)
» UPSC Essays (40)
» Model Essays (38)
» Research and Studies (4)
Economics (NCERT) Notes
» Class IX (14)
» Class X (16)
» Class XI (55)
» Class XII (53)
Economics Current (51)
International Affairs (20)
Polity and Governance (61)
Misc (77)
Select Topic »

Civil Services in India (26)
Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude (-)
» Chapters from Book (11)
» Case Studies (8)
Solved Ethics Papers (-)
» CSE - 2013 (18)
» CSE - 2014 (19)
» CSE - 2015 (17)
» CSE - 2016 (18)
» CSE - 2017 (19)
» CSE - 2018 (19)
» CSE - 2019 (19)
» CSE - 2020 (19)
» CSE - 2021 (19)
» CSE -2022 (17)
» CSE-2023 (17)
Essay and Answer Writing (-)
» Quotes (34)
» Moral Stories (18)
» Anecdotes (11)
» Beautiful Poems (10)
» Chapters from Book (5)
» UPSC Essays (40)
» Model Essays (38)
» Research and Studies (4)
Economics (NCERT) Notes (-)
» Class IX (14)
» Class X (16)
» Class XI (55)
» Class XII (53)
Economics Current (51)
International Affairs (20)
Polity and Governance (61)
Misc (77)

Indian Police Service
History
•In 1861, the British Government introduced the Indian Councils Act, 1861 introduced, a new cadre of police, called Superior Police Services, later known as the Indian Imperial Police.
•In 1902-03, a police commission was established for the Police reforms which recommended the appointment of Indians at officer level in the police.
•Indians could rise only to the ranks of Inspector of police, the senior N.C.O. position. However they were not part of Indian Imperial Police.
•From 1920, Indian Imperial Police was open to Indians and the entrance examination for the service was conducted both in India and England.
•In 1907, the Secretary of State's officers were directed to wear the letters "IP" to distinguish them from the other officers not recruited by the Secretary of State through examination.
•In 1948, a year after India gained independence; the Imperial Police was replaced by Indian Police Service (IPS).
Functions of IPS officers
•To fulfil duties based on border responsibilities, in the areas of maintenance of public peace and order, crime prevention, investigation, and detection, collection of intelligence, VIP security, counter-terrorism, border policing, railway policing, tackling smuggling, drug trafficking, economic offences, corruption in public life, disaster management, enforcement of socio-economic legislation, bio-diversity and protection of environmental laws etc.
•Leading and commanding the Indian Intelligence and Investigating Agencies like Research and Analysis Wing (R&AW), Intelligence Bureau (IB), Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI), Border Security Force (BSF), Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) etc.
•To interact and coordinate closely with the members of other All India Services and with the Indian Revenue Service and also with the Indian Armed Forces primarily with the Indian Army.
Ranks of IPS officers
•A Commissioner of Police can be of any rank of DIG and above. The other postings of IPS officers as compared to IPS officers of Delhi Police are as following:
•ADL.DCP or ASP - Additional Deputy Commissioner of Police or Additional Superintendent of Police or Deputy Commandant
•DCP or SP - Deputy Commissioner of Police or Superintendent of Police or Commandant
•DCP or SSP - Deputy Commissioner of Police or Senior Superintendent of Police or Senior Commandant
•ADL.CP or DIG - Additional Commissioner of Police or Deputy Inspector General of Police
•JCP or IGP - Joint Commissioner of Police or Inspector General of Police
•SCP or ADGP - Special Commissioner of Police or Additional Director General of Police
•CP or DGP - Commissioner of Police (State) or Director General of Police
•DIB - Director Intelligence Bureau (post held by senior most Indian Police Service officer; not a rank)
Insignia of IPS officers (Junior Rank)
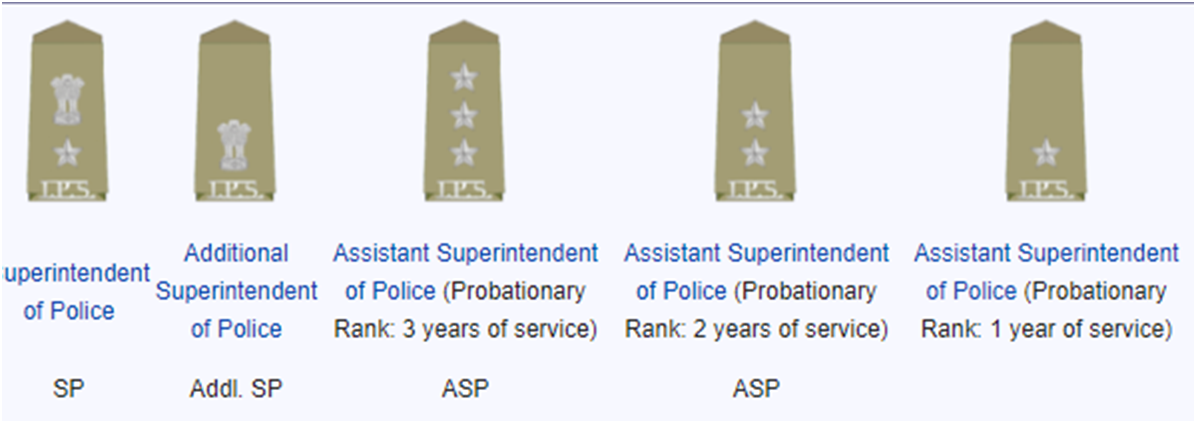
Insignia of IPS officers (Senior Rank)
Training
•The training of IPS officer recruits is conducted at Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel National Police Academy in Hyderabad.
•The authorised cadre strength of Indian Police Service is 4920. (3270 Direct Recruitment Posts and 1650 Promotional Posts).
Medals and Decorations
•Police Medal (India)
•President's Police Medal
•United Nations Medal for some officers who have participated in Indian Army United Nations peacekeeping missions.
The Issues of IPS officers
•The key functions are performed by Junior officers upto the rank of Superintend of Police (SP) or Commissioner of Police
•Too many less important and redundant posts for DIG, IG, ADG and DGs
•Political Interference
•Criminal-police nexus
•Fake encounters
•Difficult working hours
References
| Related Articles |
| Recent Articles |
